Pharmacokinetics Explained: How Your Body Processes Medication
When you take a pill, it doesn’t just disappear and start working. pharmacokinetics, the study of how your body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and eliminates drugs. Also known as ADME, it’s the science behind why some pills kick in fast, others last all day, and some can be dangerous if your liver or kidneys aren’t functioning right. This isn’t just for doctors—it’s something every person taking medication should understand. If you’re on blood pressure pills, antidepressants, or even antibiotics, your body’s handling of those drugs affects how well they work and whether you’ll have side effects.
Take drug absorption, how a medication enters your bloodstream. A pill swallowed on an empty stomach might hit your blood faster than one taken after a big meal. That’s why some meds say "take on an empty stomach"—it’s not a suggestion, it’s science. Then there’s drug distribution, how the drug moves through your body to reach its target. Some drugs stick to fat tissue, others cross the blood-brain barrier, and some can’t reach certain organs at all. This is why a drug that works for one condition might do nothing for another, even if they seem similar.
drug metabolism, how your liver breaks down the medication is where things get personal. Two people can take the same dose, but one’s liver enzymes process it quickly, the other’s slow it down. That’s why some people feel strong side effects while others don’t. If you have liver disease, like in the post about opioids and liver failure, your body can’t clear the drug properly—and that’s when toxicity builds up. And then comes drug elimination, how your kidneys or liver flush out the leftovers. If your kidneys are weak, drugs like acetazolamide or cefaclor can stick around too long, raising your risk of side effects.
None of this happens in isolation. Your age, weight, other meds, even what you ate today—all of it changes pharmacokinetics. That’s why a drug that’s safe for one person might be risky for another. The posts here show this in action: QT prolongation from antibiotics, serotonin syndrome from cough syrup, liver damage from painkillers—all tied back to how your body handles the chemicals. You’ll find guides on how to track adherence, avoid dangerous combos, and choose safer alternatives, all rooted in this same science.
Understanding pharmacokinetics doesn’t make you a pharmacist—but it does make you a smarter patient. It helps you ask the right questions, spot red flags in side effects, and know when something just doesn’t feel right. Whether you’re managing high blood pressure, diabetes, depression, or just trying to avoid a bad reaction, this is the foundation. Below, you’ll find real-world examples of how these processes play out in everyday medications—and what to do about it.
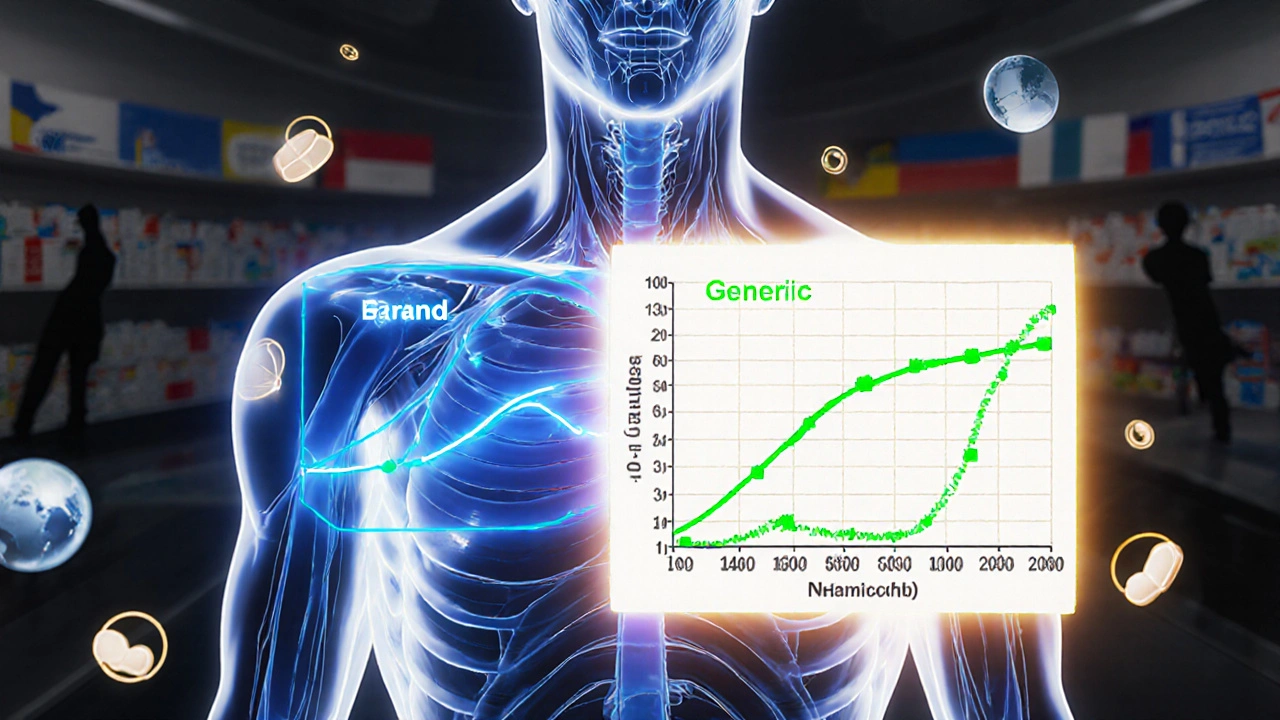
The 80-125% Rule: Understanding Bioequivalence Confidence Intervals in Generic Drugs
The 80-125% rule ensures generic drugs are absorbed similarly to brand-name versions. It's based on pharmacokinetic data, not active ingredient amounts, and is used globally to approve safe, affordable generics.
Detail